Hydraulic System
🛩️On large airplanes, a hydraulic system is used for flight control surfaces, wing flaps, spoilers, and other systems
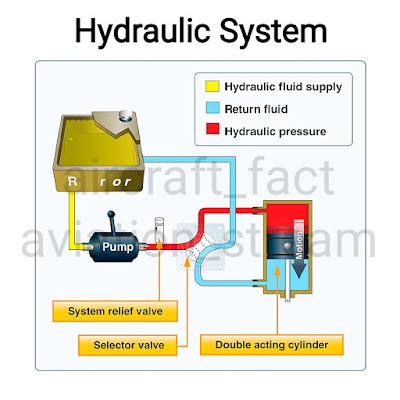
🛩️A basic hydraulic system consists of a reservoir, pump (either hand, electric or engine-driven), a filter to keep the fluid clean, a selector valve to control the direction of flow, a relief valve to relieve excess pressure, and an actuator
🛩️The hydraulic fluid is pumped through the system to an actuator or servo. A servo is a cylinder with a piston inside that turns fluid power into work and creates the power needed to move an aircraft system or flight control. Servos can be either single-acting or double-acting, based on the needs of the system. This means that the fluid can be applied to one or both sides of the servo, depending on the servo type. A single-acting servo provides power in one direction. The selector valve allows the fluid direction to be controlled. This is necessary for operations such as the extension and retraction of landing gear during which the fluid must work in two different directions. The relief valve provides an outlet for the system in the event of excessive fluid pressure in the system. Each system incorporates different components to meet the individual needs of different aircraft
➡️Subscribe us for more aircraft knowledge and aircraft fact⬅️
➡️Do Share with your Friends⬅️
Comments
Post a Comment